
- Why is Answer's plugin system designed in such a way that it seems a bit difficult to use?
- How can I implement plugin functionality using Golang?
- What exactly does Answer's plugin system do when it is compiled and packaged?
Background
You can build a Q&A community using Answer easily. However, the basic features of Answer may not sufficiently support to every use case.
Therefore, we need to design a plugin system to extend its features.
As you may know, Answer is built using React.js and Golang. Both these languages require compilation. So designing a plugin system is a bit difficult.
Goal & Features
The goal of Answer's plugin system is to provide a flexible and extendable architecture that can accommodate a wide range of use cases. Some of the key features of the plugin system include:
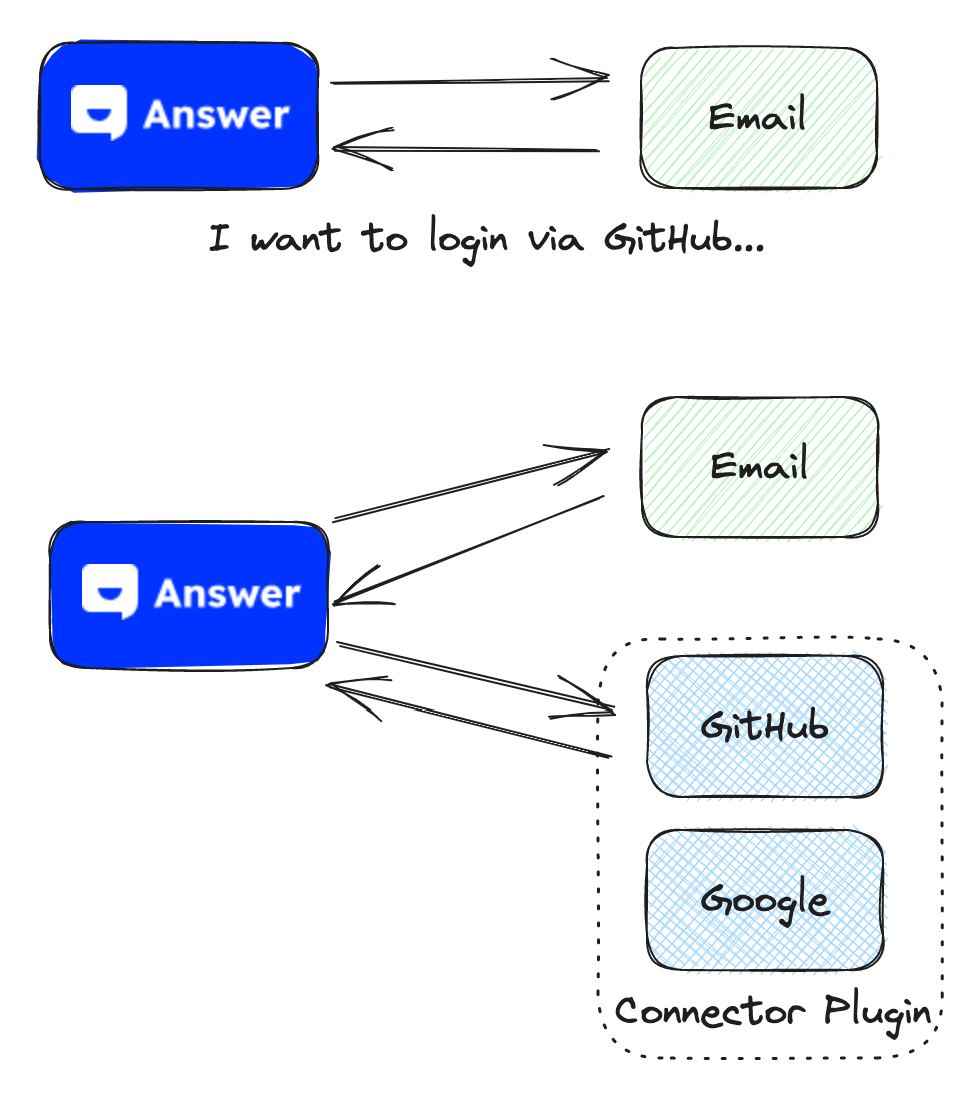
Connectors
By default, Answer supports login via email and password. Within the plugin system, developers can easily integrate other authentication, such as GitHub.
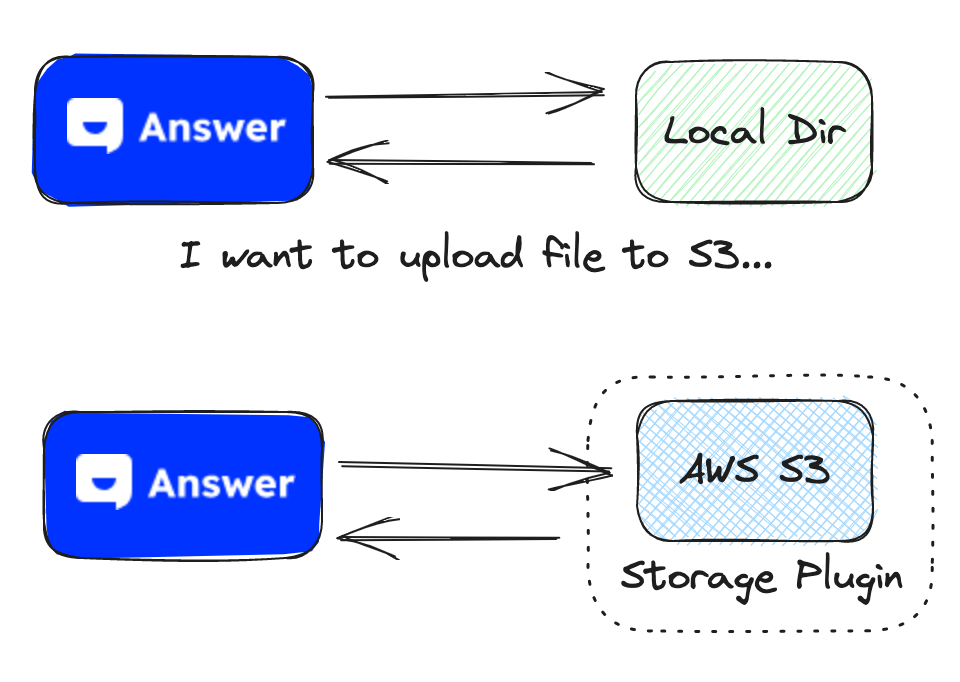
Storage
Out of the box, Answer stores files in the local file system. However, there could be scenarios where users might prefer to save their uploaded files to a cloud storage service like S3. This can be achieved by the plugin system.
Implementation
Now, let's explore how the plugin system is implemented, followed by the reasons behind our design decisions.
Details
The general process is as follows:
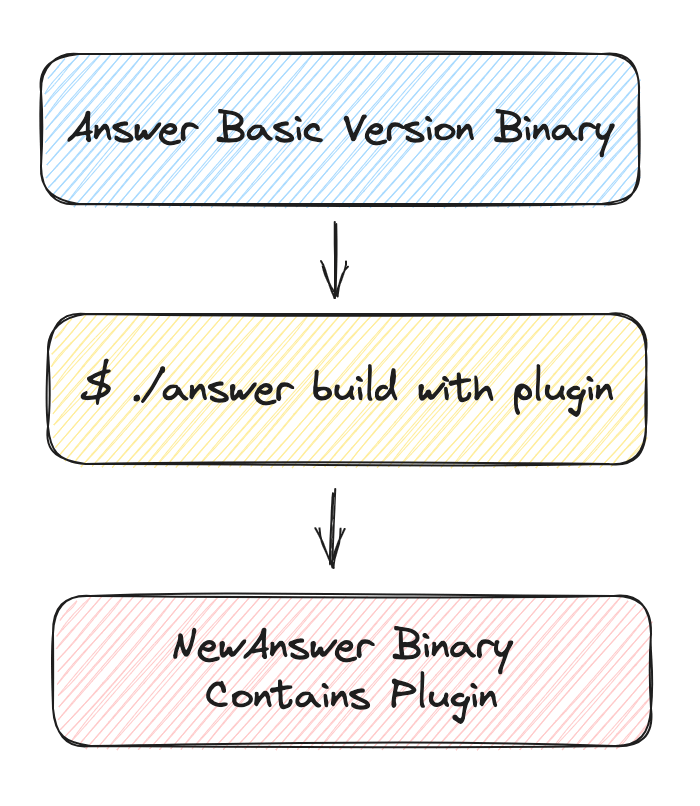
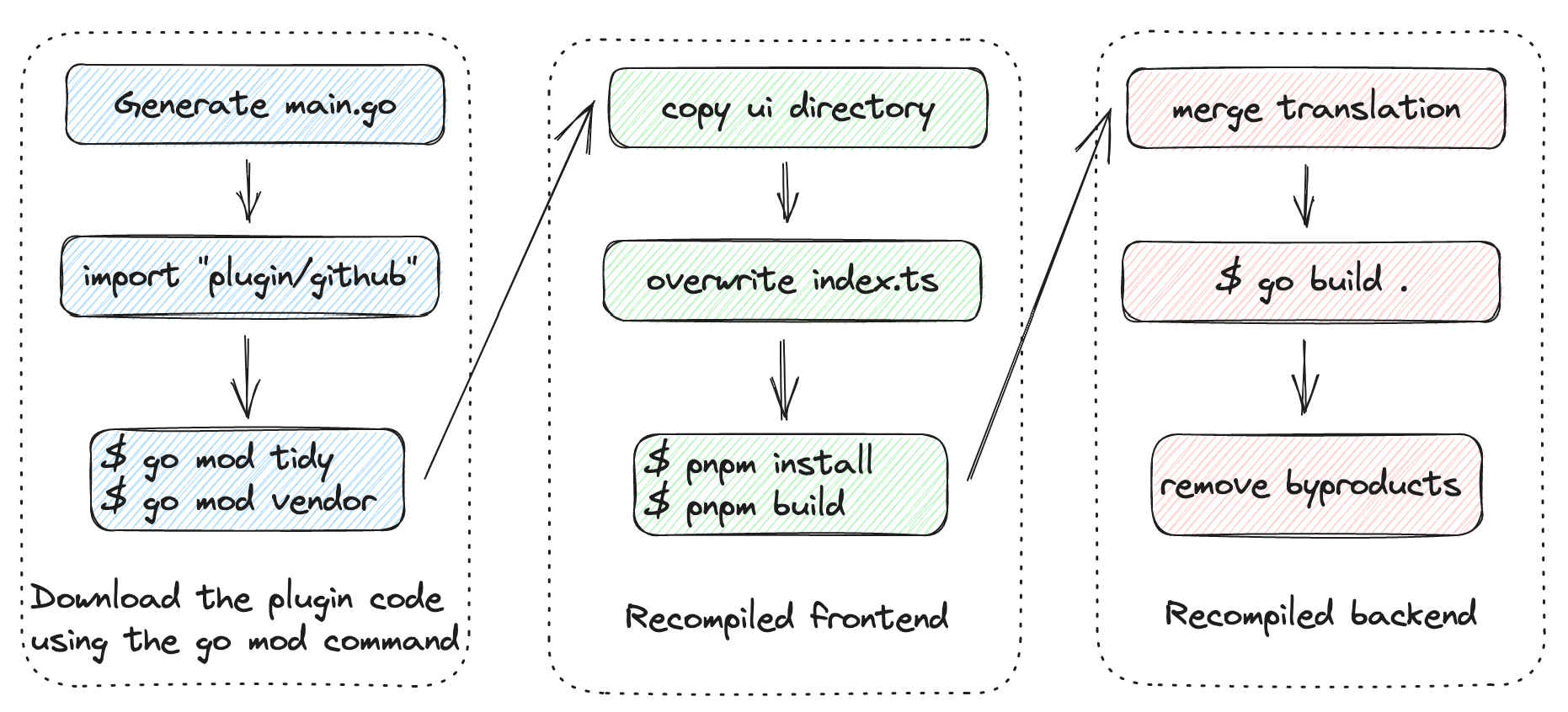
Here are the steps involved in implementing a plugin:
- Generate a
main.gofile. - Import the specific plugin list.
- Execute
go mod tidyandgo mod vendorto manage dependencies. - Copy the UI directory.
- Overwrite the
index.tsfile. - Execute
pnpm installandpnpm buildto manage the package and build the project. - Merge the
i18nfile from the plugin with the originali18nfile. - Build a new binary.
- Clean up the byproducts generated during the build process.
Reason
Here are the reasons behind our design choices:
Static Compilation
This is the main reason why the plugin system is designed this way.
React.js and Golang both these languages require compilation. They are not dynamically executable like some other scripting languages.
So the plugin system should be a static compilation, which means that the application and plugins are compiled together, resulting in a single binary that can be easily distributed and deployed.
Fixed Functionality
The plugin system allows users to add features that are fixed for their specific use cases without changing the core system. Furthermore, these functionalities persistently remain operational once they are employed. Therefore, it is sufficient to deliberate on the necessities of their incorporation at the initial stage, and subsequently, package them accordingly. In the future, we can build a Docker image that contains all official plugins, thereby enabling users to access the entire range of features. The enablement or disablement of these functionalities can be managed through the plugin control interface.
Extension
The most important capability of a plugin system is its extensibility. A program can't provide all the functions that every user wants. However, with a plugin system, users can develop their plugins to help them achieve the functions that they want.
Reference
The Caddy is a great open-source software that inspired the design of the Answer plugin system. Caddy is a web server that allows developers to extend its functionality using plugins. Using xcaddy can easy to make custom builds of the Caddy Web Server.
More
In this blog post, we discussed the design and implementation of the plugin system for Answer, a popular open-source Q&A platform. We discussed the motivation behind the design, and the features and principles of the plugin system, and provided a step-by-step guide on implementation. If you are interested in developing plugins for Answer, please feel free to leave us a comment. We will also write an article on how to implement an Answer plugin from scratch, so stay focused!